<- previous index next ->
From "A Collection of 2D Elliptic Problems for Testing
Adaptive Algorithms" by William F. Mitchell
1. Solutions of the form
U(x,y)=2^4p x^p (x-1)^p y^p (y-1)^p for p=4
PDE Uxx(x,y) + Uyy(x,y) = f(x,y)
boundary unit square
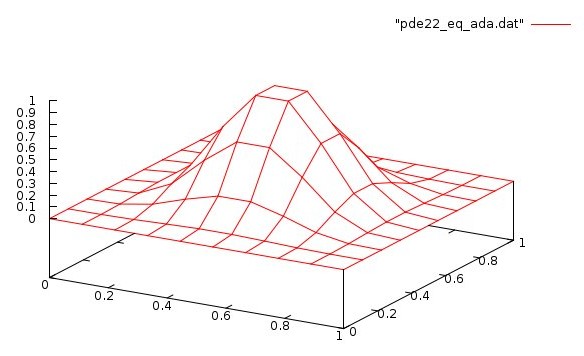 pde22_eq.adb
pde22_eq_ada.out
pde22_eq_ada.dat
pde22_eq_ada.plot
pde22_eq_ada.sh
pde22_eq.c
pde22_eq_c.out
pde22_eq_c.dat
pde22_eq_c.plot
pde22_eq_c.sh
pde22_eq.java
pde22_eq_java.out
pde22_eq_java.dat
pde22_eq_java.plot
pde22_eq_java.sh
pde22_eq.f90
pde22_eq_f90.out
pde22_eq_f90.dat
pde22_eq_f90.plot
pde22_eq_f90.sh
pde22_eq.adb
pde22_eq_ada.out
pde22_eq_ada.dat
pde22_eq_ada.plot
pde22_eq_ada.sh
pde22_eq.c
pde22_eq_c.out
pde22_eq_c.dat
pde22_eq_c.plot
pde22_eq_c.sh
pde22_eq.java
pde22_eq_java.out
pde22_eq_java.dat
pde22_eq_java.plot
pde22_eq_java.sh
pde22_eq.f90
pde22_eq_f90.out
pde22_eq_f90.dat
pde22_eq_f90.plot
pde22_eq_f90.sh
Then U(x,y)=2^4p x^p (x-1)^p y^p (y-1)^p for p=10
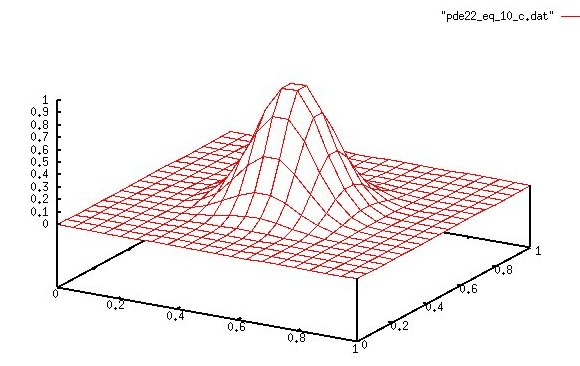 pde22_eq_10.c
pde22_eq_10_c.out
pde22_eq_10_c.dat
pde22_eq_10_c.plot
pde22_eq_10_c.sh
pde22_eq_10.c
pde22_eq_10_c.out
pde22_eq_10_c.dat
pde22_eq_10_c.plot
pde22_eq_10_c.sh
Then U(x,y)=4*(x-1)*(x-3)*(x-3)*(y-1)*(y-3)*(y-3) p=9
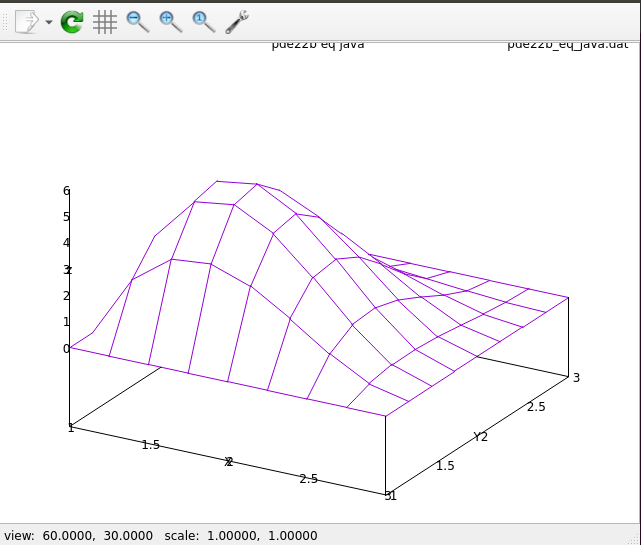 pde22b_eq.java source code
simeq.java source code
rderiv.java source code
pde22b_eq_java.out
pde22b_eq_java.dat
pde22b_eq_java.plot
pde22b_eq_java.sh
pde22b_eq.java source code
simeq.java source code
rderiv.java source code
pde22b_eq_java.out
pde22b_eq_java.dat
pde22b_eq_java.plot
pde22b_eq_java.sh
Then U(x,y)=5*(x*x+x)*(y*y+y) p=9
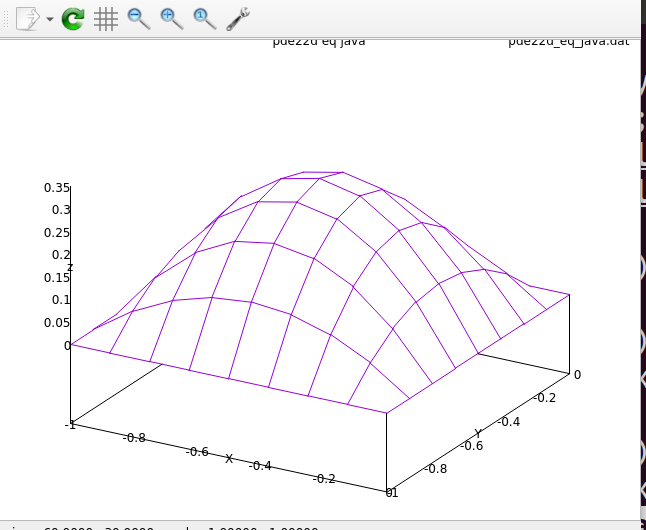 pde22d_eq.java
pde22d_eq_java.out
pde22d_eq_java.dat
pde22d_eq_java.plot
pde22d_eq_java.sh
pde22d_eq.java
pde22d_eq_java.out
pde22d_eq_java.dat
pde22d_eq_java.plot
pde22d_eq_java.sh
2. Solutions of the form
alpha = Pi/omega
r = sqrt(x^2+y^2)
theta = atan2(y,x) 0..2Pi
U(x,y)=r^alpha * sin(alpha*theta)
PDE Uxx(x,y) + Uyy(x,y) = 0
boundary x -1..1, y -1..1
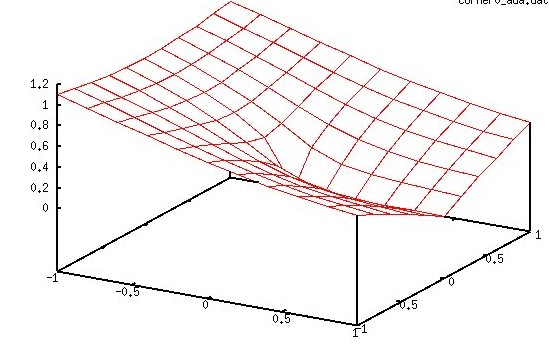 Exact solution
Exact solution
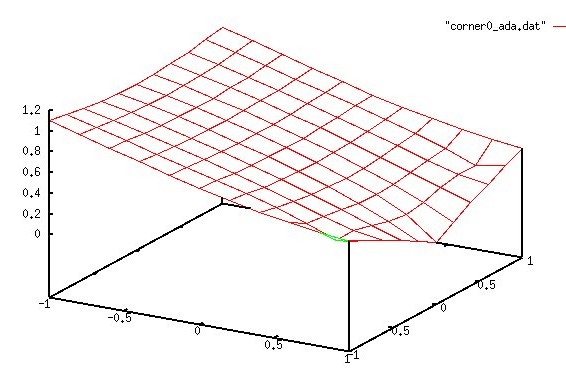 nx=11, ny=11 uniformly spaced, computed solution
corner0.adb
corner0_ada.out
corner0_ada.dat
corner0_ada.plot
corner0_ada.sh
corner0.c
corner0_c.out
corner0_c.dat
corner0_c.plot
corner0_c.sh
corner0.java
corner0_java.out
corner0_java.dat
corner0_java.plot
corner0_java.sh
corner0.f90
corner0_f90.out
corner0_f90.dat
corner0_f90.plot
corner0_f90.sh
nx=11, ny=11 uniformly spaced, computed solution
corner0.adb
corner0_ada.out
corner0_ada.dat
corner0_ada.plot
corner0_ada.sh
corner0.c
corner0_c.out
corner0_c.dat
corner0_c.plot
corner0_c.sh
corner0.java
corner0_java.out
corner0_java.dat
corner0_java.plot
corner0_java.sh
corner0.f90
corner0_f90.out
corner0_f90.dat
corner0_f90.plot
corner0_f90.sh
Makefile and other files for programs listed above
Makefile_spde
nuderiv.adb
inverse.adb
simeq.adb
real_arrays.ads
real_arrays.adb
nuderiv.c
inverse.c
simeq.c
mpf_nuderivd.c
mpf_inverse.c
nuderiv.java
inverse.java
simeq.java
nuderiv.f90
inverse.f90
simeq.f90
Have gnuplot installed to get plots.
Have gnat installed for .adb
Have gcc installed for .c
Have Java installed for .java
Have gfortran installed for .f90
PDE for Turbulence and Diffusion
pde_turbulence.pdf
diffusion_equation
Generic_scalar_transport_equation
Unusual geometries and using all differentials

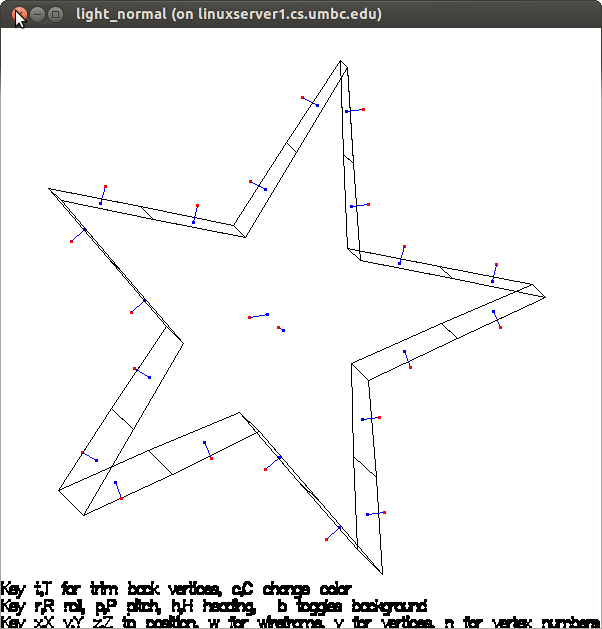 The red dot is the positive direction of the normal to the surface.
Plotted with light_normal.c to be sure all surfaces have normal
pointing out. This is needed to be able to determine if a
point is inside the volume and process Neumann boundary conditions.
poly43.txt
All 4th order derivatives in 3 dimensions.
pde_star3t.java
Used in pde_star3t.java.
The red dot is the positive direction of the normal to the surface.
Plotted with light_normal.c to be sure all surfaces have normal
pointing out. This is needed to be able to determine if a
point is inside the volume and process Neumann boundary conditions.
poly43.txt
All 4th order derivatives in 3 dimensions.
pde_star3t.java
Used in pde_star3t.java.
<- previous index next ->
-
CMSC 455 home page
-
Syllabus - class dates and subjects, homework dates, reading assignments
-
Homework assignments - the details
-
Projects -
-
Partial Lecture Notes, one per WEB page
-
Partial Lecture Notes, one big page for printing
-
Downloadable samples, source and executables
-
Some brief notes on Matlab
-
Some brief notes on Python
-
Some brief notes on Fortran 95
-
Some brief notes on Ada 95
-
An Ada math library (gnatmath95)
-
Finite difference approximations for derivatives
-
MATLAB examples, some ODE, some PDE
-
parallel threads examples
-
Reference pages on Taylor series, identities,
coordinate systems, differential operators
-
selected news related to numerical computation
 pde22_eq.adb
pde22_eq_ada.out
pde22_eq_ada.dat
pde22_eq_ada.plot
pde22_eq_ada.sh
pde22_eq.c
pde22_eq_c.out
pde22_eq_c.dat
pde22_eq_c.plot
pde22_eq_c.sh
pde22_eq.java
pde22_eq_java.out
pde22_eq_java.dat
pde22_eq_java.plot
pde22_eq_java.sh
pde22_eq.f90
pde22_eq_f90.out
pde22_eq_f90.dat
pde22_eq_f90.plot
pde22_eq_f90.sh
pde22_eq.adb
pde22_eq_ada.out
pde22_eq_ada.dat
pde22_eq_ada.plot
pde22_eq_ada.sh
pde22_eq.c
pde22_eq_c.out
pde22_eq_c.dat
pde22_eq_c.plot
pde22_eq_c.sh
pde22_eq.java
pde22_eq_java.out
pde22_eq_java.dat
pde22_eq_java.plot
pde22_eq_java.sh
pde22_eq.f90
pde22_eq_f90.out
pde22_eq_f90.dat
pde22_eq_f90.plot
pde22_eq_f90.sh
 pde22_eq_10.c
pde22_eq_10_c.out
pde22_eq_10_c.dat
pde22_eq_10_c.plot
pde22_eq_10_c.sh
pde22_eq_10.c
pde22_eq_10_c.out
pde22_eq_10_c.dat
pde22_eq_10_c.plot
pde22_eq_10_c.sh
 pde22b_eq.java source code
simeq.java source code
rderiv.java source code
pde22b_eq_java.out
pde22b_eq_java.dat
pde22b_eq_java.plot
pde22b_eq_java.sh
pde22b_eq.java source code
simeq.java source code
rderiv.java source code
pde22b_eq_java.out
pde22b_eq_java.dat
pde22b_eq_java.plot
pde22b_eq_java.sh
 pde22d_eq.java
pde22d_eq_java.out
pde22d_eq_java.dat
pde22d_eq_java.plot
pde22d_eq_java.sh
pde22d_eq.java
pde22d_eq_java.out
pde22d_eq_java.dat
pde22d_eq_java.plot
pde22d_eq_java.sh
 Exact solution
Exact solution
 nx=11, ny=11 uniformly spaced, computed solution
corner0.adb
corner0_ada.out
corner0_ada.dat
corner0_ada.plot
corner0_ada.sh
corner0.c
corner0_c.out
corner0_c.dat
corner0_c.plot
corner0_c.sh
corner0.java
corner0_java.out
corner0_java.dat
corner0_java.plot
corner0_java.sh
corner0.f90
corner0_f90.out
corner0_f90.dat
corner0_f90.plot
corner0_f90.sh
nx=11, ny=11 uniformly spaced, computed solution
corner0.adb
corner0_ada.out
corner0_ada.dat
corner0_ada.plot
corner0_ada.sh
corner0.c
corner0_c.out
corner0_c.dat
corner0_c.plot
corner0_c.sh
corner0.java
corner0_java.out
corner0_java.dat
corner0_java.plot
corner0_java.sh
corner0.f90
corner0_f90.out
corner0_f90.dat
corner0_f90.plot
corner0_f90.sh

 The red dot is the positive direction of the normal to the surface.
Plotted with light_normal.c to be sure all surfaces have normal
pointing out. This is needed to be able to determine if a
point is inside the volume and process Neumann boundary conditions.
poly43.txt
All 4th order derivatives in 3 dimensions.
pde_star3t.java
Used in pde_star3t.java.
The red dot is the positive direction of the normal to the surface.
Plotted with light_normal.c to be sure all surfaces have normal
pointing out. This is needed to be able to determine if a
point is inside the volume and process Neumann boundary conditions.
poly43.txt
All 4th order derivatives in 3 dimensions.
pde_star3t.java
Used in pde_star3t.java.